What is electricity and how is it made?
Electricity is everywhere! From powering your TV and favourite video games, to keeping your phone alive and switching on the little light in your fridge, most of us interact with electricity every day. Even in the natural world, electricity is present. It is used as a means to hunt by electric eels and can be seen in the sky above us during a storm.
We have already discussed the history of the electricity network and when it was invented. In this guide we are going to dive into how electricity works and the journey it takes to get safely into your home.
So how do we make electricity? To put it simply, electricity is a secondary energy source that we can convert from primary sources of energy such as coal, oil, nuclear power and gas. But really, to understand how it all works, we need to take a step back and look at the science behind electricity.
Electricity and Atoms
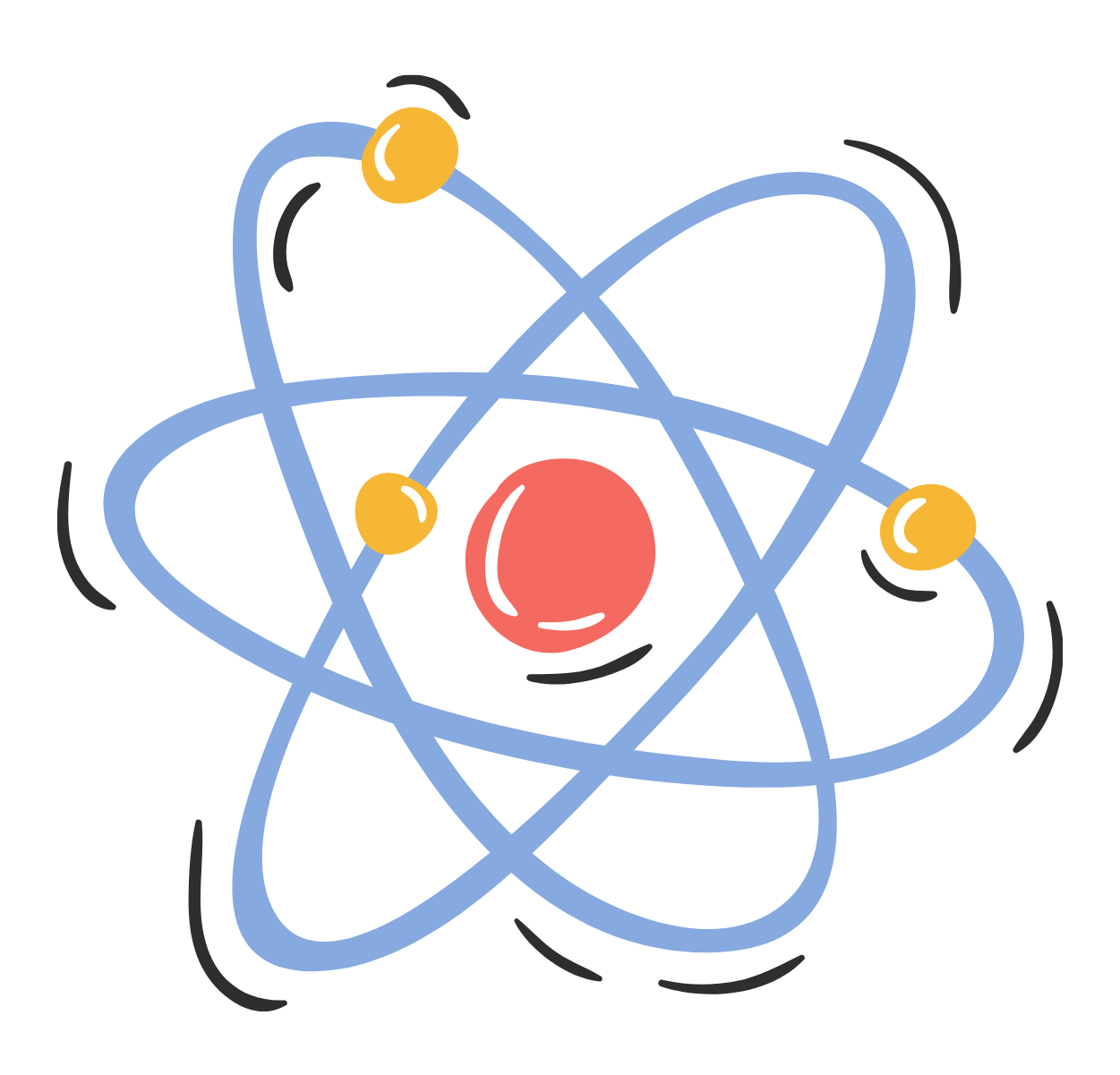
Atoms are the basic building blocks of everything and everyone. Everything is made up of miniscule atoms, including electricity. And atoms are made up of even smaller elements, these are:
- Protons
- Electrons
- Neutrons
The protons and neutrons are at the centre of the atom, whilst the electrons revolve around the centre – kind of like excited dogs, or energetic children.
The protons in the middle of the atom (positive) and electrons revolving around the side (negative) are attracted to each other and each carries an electrical charge. The positive charge of the protons is equal to the negative charge of the electrons, whilst the neutrons stay neutral.
Electricity is a flow of electrons around a circuit. So, when electrical and magnetic forces move electrons from one atom to another, an electrical current is formed. And bam! You have the power source of electricity.
What Are the Sources of Electricity?
So, we now understand the basics of how electricity is created, but how do people generate it? This is where our primary sources of energy come into play. There are renewable sources of energy such as wind energy and hydropower, and other forms like coal and gas. For most sources they serve the same purpose - to turn the turbines that control the generator, which in turn makes electricity.
For context, 42% of the UKs electricity came from renewable sources in 2020, with clean power generating more power than fossil fuels for the first time.
The Sources of Electricity Explained
How Does Solar Power Work? - Solar panels are used in order to convert energy from the sun into power. When light from the sun hits the solar panel, they knock electrons off the silicon atoms.
How Does Hydropower Work? - Flowing water spins the turbine in order to generate hydroelectric power. Usually, hydroelectric dams are used which direct the water through the turbine, but the sea’s tides and rivers can also be used.
How Do We Get Electricity from Coal? - Coal is mined into a fine powder and blown into a boiler that burns at an extremely high temperature. The boiler heats water which in turn creates steam. This steam travels through the turbines that are in turn connected to a generator. When the generator is rotated in a strong magnetic field, electricity is created.
How Do We Get Electricity from Wind Turbines? - As you’ve probably guessed, wind turbines use wind to make electricity. The propellers of the wind turbine spin a shaft, which connects to the generator.
How Does Nuclear Power Work? - Nuclear energy comes from the energy in the core of an atom. Using a process called nuclear fission in the reactor core boils water into steam, which, again, turns the blades of a steam turbine and drive the generators to make electricity.
How Are Turbines Used to Generate Electricity?
For every fuel, we need a turbine in order to gain electricity, and most follow the same principle:
- A turbine spins magnets surrounded by copper wire
- This generates the flow of electrons across atoms
- As a result, electricity is created.

Power stations convert fuels into electricity.
Coal and gas heat water, which creates steam that turns the turbine.
Hydropower and wind can also be used to turn the turbine and generate the electricity.
Then you have solar panels. These work a bit differently and generate electrical power by converting solar radiation into electricity using semiconductors.

How Does Electricity Get to Your Home?
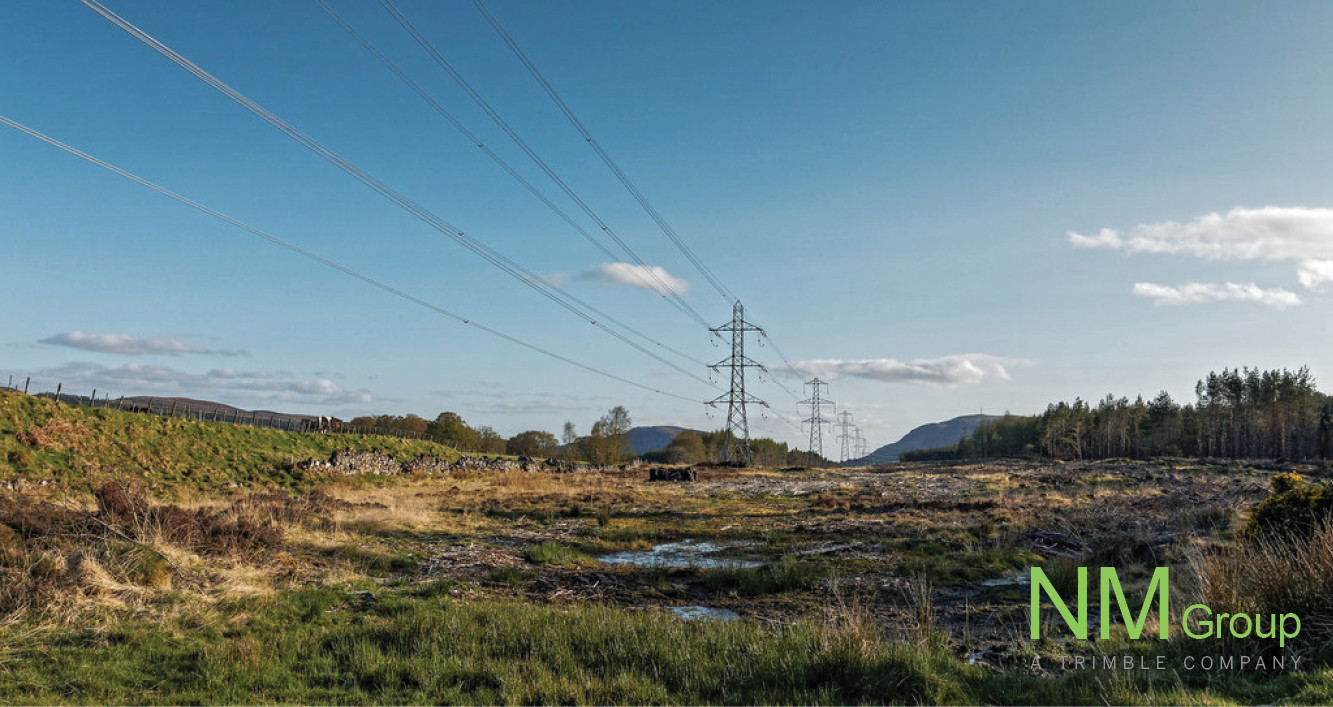
The electricity grid is the short answer as to how electricity travels to your home. The longer answer is that electricity is delivered to your house via a complex system of transmissions and distribution power lines. Thousands of miles of high-voltage power lines are placed across the country in order to connect power plants to the rest of the nation.
There are high voltage power lines and lower voltage distribution lines. The high voltage power lines are the large structures (pylons) you see, which allows electricity to travel efficiently over long distances. Then transformers are used to transform the voltage down to a voltage that households can use, in the UK this is 230 V.

Where Does NM Group Come In?
NM Group optimises the performance of power networks by remotely sensing and servicing the position of power lines and the electrical grid. From mapping and presenting spatial data on an electrical network through to modelling and displaying 3D network environment.
In a nutshell, we help to ensure that generated electricity travels safely into your home, to power your lights, fridge, games console and TV. Learn more about NM Group here.